Question 25 of 25
100 % Complete
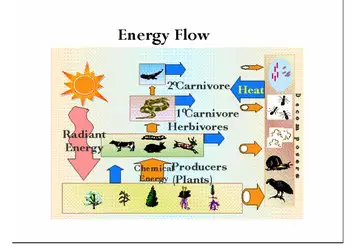
There is risk of damaging the carbon cycle (Global Warming), by:
Read the following passage from KidsGeo.com regarding the Carbon Cycle:
“…This important balance [of carbon] has been altered significantly in the past century as
humans have begun using fossil fuels to produce energy. By burning the Earth’s store of carbon,
mankind is able to create the energy needed to operate our communities. However, we must be
careful as we do so. By releasing more carbon into the atmosphere than is being locked up, we
risk causing damage to the delicate carbon cycle.”
The Carbon Cycle. (2013). Geography for kids, The study of our Earth. Retrieved October 17, 2013, from http://www.kidsgeo.com/geography-for-kids/0146-ocean-tides.php
There is risk of damaging the carbon cycle (Global Warming), by:
A. Getting energy to operate our communities
B. Releasing more carbon into the atmosphere
C. Producing energy
D. Digging up fossil fuels
B. Releasing more carbon into the atmosphere